adrenal support

free shipping over $100 (USA & Canada)
1-877-937-4372 the pet expert hotline

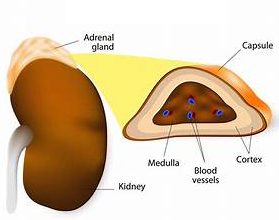
Hyperadrenocorticism arises from the overproduction of glucocorticoid hormones by one or both adrenal glands. In this scenario, it’s also known as Cushing’s disease. This condition can also come as the result of chronic or excessive administration of steroid medications, which is then classified as Cushing’s syndrome. In atypical cases, other adrenal hormones, such as sex hormones, may also be elevated.
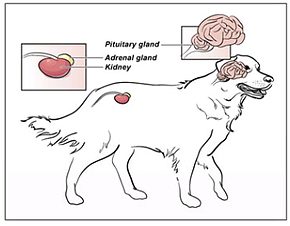
1) Pituitary-dependent hyperadrenocorticism (PHD): This condition develops when a tumor of the pituitary gland produces high levels of adrenocorticotropic hormones (ACTH), which subsequently cause the adrenal glands to become overactive.
2) Iatrogenic hyperadrenocorticism: This condition is the result of prolonged or excessive administration of glucocorticoid medications. The adjective iatrogenic refers to an illness or disease brought on by medication or treatment.
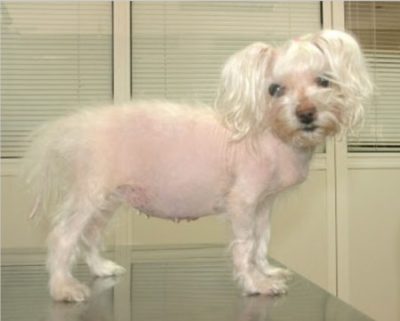
Some of the signs include increased thirst, urination, and appetite. Symmetrical thinning or loss of hair may also be visible. Thinning or darkening of the skin, skin that bruises easily, panting, and heat intolerance. Urinary tract and skin infections are also possible symptoms.
The diagnostic Cushing’s test for dogs is based on the history of prolonged exposure to steroid medication and can be confirmed through laboratory evidence of low adrenal gland function. Since no single clinical sign is specific to the disease, the diagnosis of Cushing’s disease requires laboratory testing and other diagnostic methods. These may include the ACTH response test, urine cortisol/creatinine ratio, and the modified high-dose dexamethasone test. Unfortunately, the results for dog Cushing’s disease tests may not be clear. This only adds to the challenge of accurately diagnosing this disease.
If your dog has Cushing’s syndrome, it can be treated by slow, tapered withdrawal of steroid medications. PHD can be treated with medication. If adrenal tumors are present, these may be treated by surgical removal or medication.
Hyperadrenocorticism in dogs requires constant visits to the vet because this disease is complicated to treat. Your pet will need frequent adjustment of their medication dosage and constant laboratory testing.
The drugs used to treat this disorder are potentially toxic, such as Mitotane. It is very important to understand the side effects of the prescribed drugs. The medication may not reverse the clinical signs, and hyperadrenocorticism may decrease the life span of the dog.
Supraglan for Dogs: This supplement is a balancing formula that helps control adrenal hormones. It also provides support for pituitary gland dysfunction. You can find one success story right here.
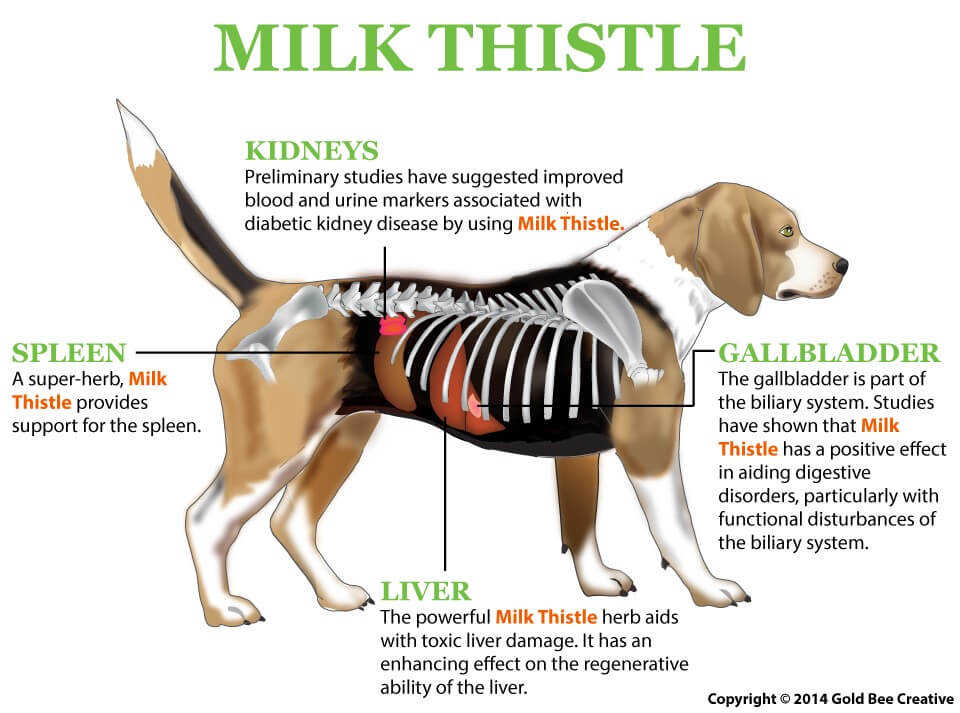
NHV Milk Thistle for Dogs: Studies have shown that milk thistle can enhance the suppression of ACTH secretion, and can restore glucocorticoid sensitivity in dogs with Cushing’s disease as a result of this action. It also detoxifies the liver and kidneys by helping to remove toxins that can build up in your pet’s system from pharmaceuticals or chemical-laden foods. Milk thistle can improve liver and kidney function, support regeneration of the liver, and even provide support for overworked kidneys. It’s also known for its antioxidant properties and may offer the benefit of anti-cancer support.
Multi Essentials for Dogs: This is a plant-based multivitamin with herbal extracts that helps to fill nutritional voids, aid digestion, and enhance nutrient absorption. Multi Essentials also helps stimulate the metabolism, reduces fatigue, increases energy and promotes a healthy coat and skin for your pet.
adrenal support

Natural Cushing’s Disease, Adrenal, and Addison’s Support for dogs
buy 2 and save $3
3 month supply for a small to medium size
Our vet-formulated canine adrenal and Cushing’s support product can help your dog get the nutrients they need to balance vital hormones and promote healthy adrenal gland function.

Our vet-formulated canine adrenal and Cushing’s support product can help your dog get the nutrients they need to balance vital hormones and promote healthy adrenal gland function.
Dogs with adrenal disorders like Cushing’s and Addison’s may have other health issues that can affect a pup’s quality of life. Supraglan™ canine adrenal support supplements can help these dogs.
The overproduction of cortisol in canines with Cushing’s disease can cause excessive thirst, urination, and appetite. These symptoms can result in other side effects like obesity, fat pads near the neck, and low energy.
Cushing’s disease may sometimes be the result of continued steroid use or a tumor on the adrenal gland. Your vet’s treatment plan for Cushing’s or other canine adrenal support will likely include medication and potential surgery in cases where a tumor is present. Feeding Supraglan™ supplements to your dog alongside the vet’s treatment will help them through the process.
Our adrenal supplements can help dogs undergoing treatment for diseases like Cushing’s with powerful and natural ingredients that help improve adrenal gland function, regulate metabolism, and promote good digestion.
Supraglan™ is formulated with ingredients like borage which help to balance a dog’s endocrine system, astragalus for its anti-inflammatory effects, eleuthero to help regulate adrenal gland function, and other potent ingredients key in supporting their overall health.
For additional support, see NHV’s other adrenal disorder supplements and kits.
All of NHV’s canine adrenal support products are ethically sourced, free of GMOs, and tested by a third party to ensure concentration and product quality. Find natural solutions you can trust in your dog’s health regimen when you shop at NHV.
Borage – Helps to balance endocrine system functions, restore the adrenal cortex, and eliminate toxins
Astragalus – Contains anti-inflammatory properties and balance your dog’s immunity
Bistort – Contains anti-inflammatory properties that benefit the liver and kidneys
Eleuthero – Helps balance (Acts on, supports, aids, assists) adrenal gland function and may help balance metabolism
Wild Yam – Helps balance and normalizes liver function
Licorice – Contains anti-inflammatory properties and balance adrenal gland function
Dandelion – Helps balance liver secretions and promotes good digestion
Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
To be taken twice daily. Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. This is the minimum dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb = 0.5 ml
16 - 30 lb = 1.0 ml
31 - 45 lb = 1.5 ml
46 - 60 lb = 2.0 ml
61 - 75 lb = 2.5 ml
Over 75 lb = 3.0 ml
For small animals (rabbits, ferrets), avians and reptiles use 1 drop for every 2 lb of body weight.
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provided and place the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth. Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken or yogurt or a favorite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and well-being of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Do not use Supraglan in pregnant or nursing animals. Speak to your vet before using our products. A second visit is recommended if your pet’s condition does not improve, or deteriorates after continued use of the supplements.
All information provided by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.
Dogs with adrenal disorders like Cushing’s and Addison’s may have other health issues that can affect a pup’s quality of life. Supraglan™ canine adrenal support supplements can help these dogs.
The overproduction of cortisol in canines with Cushing’s disease can cause excessive thirst, urination, and appetite. These symptoms can result in other side effects like obesity, fat pads near the neck, and low energy.
Cushing’s disease may sometimes be the result of continued steroid use or a tumor on the adrenal gland. Your vet’s treatment plan for Cushing’s or other canine adrenal support will likely include medication and potential surgery in cases where a tumor is present. Feeding Supraglan™ supplements to your dog alongside the vet’s treatment will help them through the process.
Our adrenal supplements can help dogs undergoing treatment for diseases like Cushing’s with powerful and natural ingredients that help improve adrenal gland function, regulate metabolism, and promote good digestion.
Supraglan™ is formulated with ingredients like borage which help to balance a dog’s endocrine system, astragalus for its anti-inflammatory effects, eleuthero to help regulate adrenal gland function, and other potent ingredients key in supporting their overall health.
For additional support, see NHV’s other adrenal disorder supplements and kits.
All of NHV’s canine adrenal support products are ethically sourced, free of GMOs, and tested by a third party to ensure concentration and product quality. Find natural solutions you can trust in your dog’s health regimen when you shop at NHV.
Borage – Helps to balance endocrine system functions, restore the adrenal cortex, and eliminate toxins
Astragalus – Contains anti-inflammatory properties and balance your dog’s immunity
Bistort – Contains anti-inflammatory properties that benefit the liver and kidneys
Eleuthero – Helps balance (Acts on, supports, aids, assists) adrenal gland function and may help balance metabolism
Wild Yam – Helps balance and normalizes liver function
Licorice – Contains anti-inflammatory properties and balance adrenal gland function
Dandelion – Helps balance liver secretions and promotes good digestion
Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
To be taken twice daily. Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. This is the minimum dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb = 0.5 ml
16 - 30 lb = 1.0 ml
31 - 45 lb = 1.5 ml
46 - 60 lb = 2.0 ml
61 - 75 lb = 2.5 ml
Over 75 lb = 3.0 ml
For small animals (rabbits, ferrets), avians and reptiles use 1 drop for every 2 lb of body weight.
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provided and place the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth. Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken or yogurt or a favorite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and well-being of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Do not use Supraglan in pregnant or nursing animals. Speak to your vet before using our products. A second visit is recommended if your pet’s condition does not improve, or deteriorates after continued use of the supplements.
All information provided by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.
liver support

Support for liver and kidney detox and cancer support in dogs
3 month supply for a small to medium size pet
These effects help to remove chemicals and toxins that can accumulate in your dog’s system. It is one of the few herbs with no equivalent in conventional medicine.


These effects help to remove chemicals and toxins that can accumulate in your dog’s system. It is one of the few herbs with no equivalent in conventional medicine.

Milk Thistle is a powerful herb that’s been used by humans for thousands of years. The active ingredient, silymarin, has been shown through scientific studies to possess strong anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and detoxifying properties. It also promotes cellular regeneration and repair.
This supplement by NHV Natural Pet Products uses 100% natural milk thistle to support dogs through liver and kidney conditions in addition to conventional treatment by their veterinarian.
Milk thistle improves kidney function due to the damage from:
The extraordinary antioxidant properties of milk thistle for dog extract acts to:
The scientific name for milk thistle is Silybum Marianum. It’s also referred to as wild artichoke and holy thistle.
Milk thistle for dog liver support can be used in conjunction with conventional treatments and is glycerin based and safe for long-term use. You can read more about the benefits of using milk thistle on Dr. Hillary Cook’s blog.
At NHV, all of our products including milk thistle for dog kidney support are plant-based and make excellent proactive support for many health conditions. If you have questions on milk thistle for dogs or any of our holistic supplements, you can ask an expert at NHV because we put your pet first when it comes to health and healing naturally.
Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
To be taken twice daily. Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. This is the minimum dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb = 0.5 ml
16 - 30 lb = 1.0 ml
31 - 45 lb = 1.5 ml
46 - 60 lb = 2.0 ml
61 - 75 lb = 2.5 ml
Over 75 lb = 3.0 ml
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provide and places the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth.
Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken or yogurt or a favourite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and wellbeing of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Do not use Milk Thistle in pregnant or nursing animals. Speak to your vet before using our products. A second visit is recommended if your pet’s condition does not improve, or deteriorates after continued use of the supplements.
All information provided by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.
Milk Thistle is a powerful herb that’s been used by humans for thousands of years. The active ingredient, silymarin, has been shown through scientific studies to possess strong anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and detoxifying properties. It also promotes cellular regeneration and repair.
This supplement by NHV Natural Pet Products uses 100% natural milk thistle to support dogs through liver and kidney conditions in addition to conventional treatment by their veterinarian.
Milk thistle improves kidney function due to the damage from:
The extraordinary antioxidant properties of milk thistle for dog extract acts to:
The scientific name for milk thistle is Silybum Marianum. It’s also referred to as wild artichoke and holy thistle.
Milk thistle for dog liver support can be used in conjunction with conventional treatments and is glycerin based and safe for long-term use. You can read more about the benefits of using milk thistle on Dr. Hillary Cook’s blog.
At NHV, all of our products including milk thistle for dog kidney support are plant-based and make excellent proactive support for many health conditions. If you have questions on milk thistle for dogs or any of our holistic supplements, you can ask an expert at NHV because we put your pet first when it comes to health and healing naturally.

Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
To be taken twice daily. Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. This is the minimum dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb = 0.5 ml
16 - 30 lb = 1.0 ml
31 - 45 lb = 1.5 ml
46 - 60 lb = 2.0 ml
61 - 75 lb = 2.5 ml
Over 75 lb = 3.0 ml
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provide and places the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth.
Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken or yogurt or a favourite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and wellbeing of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Do not use Milk Thistle in pregnant or nursing animals. Speak to your vet before using our products. A second visit is recommended if your pet’s condition does not improve, or deteriorates after continued use of the supplements.
All information provided by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.
multivitamin support

Herbal Digestive Aid, Energy Booster, and Multivitamin for Dogs
buy 2 and save $3
3 month supply for a small to medium size pet
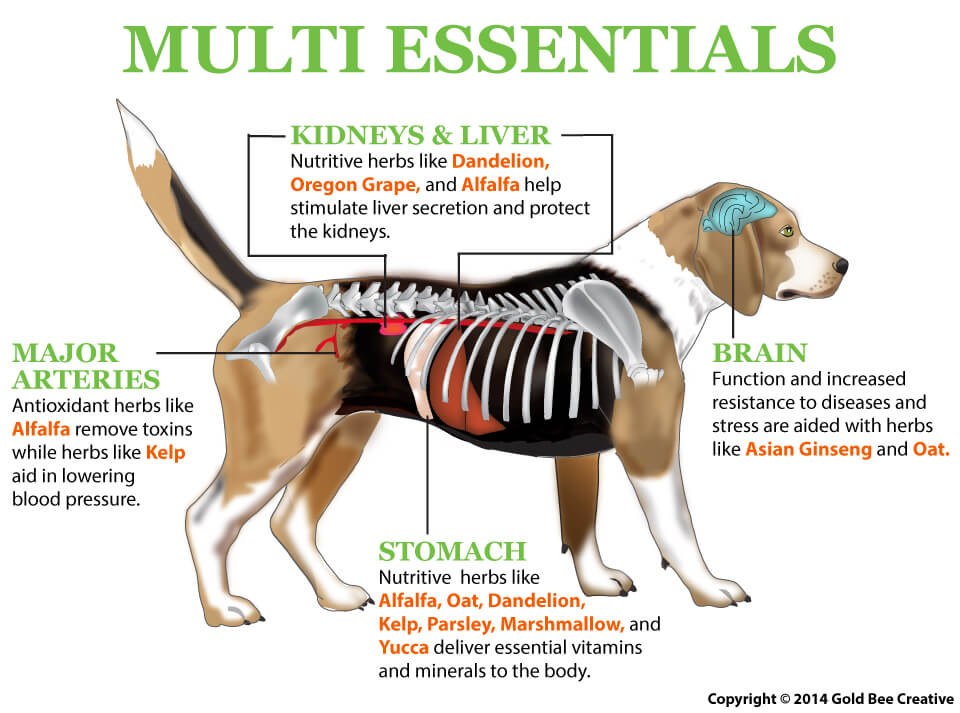
NHV’s multivitamins for dogs targets the brain, stomach, major arteries, kidneys, and liver with a powerful blend of herbal support.


NHV’s multivitamins for dogs targets the brain, stomach, major arteries, kidneys, and liver with a powerful blend of herbal support.

Millions of people take multivitamins daily to support their health, and it only makes sense our canine companions can benefit just as much. This 100% natural plant-based liquid blend can help your dog with nutritional deficiencies.
Signs of Possible Vitamin Deficiency in Dogs
NHV’s Multi-Essentials are packed with herbs that are rich in vitamins and minerals. This vet-formulated blend is designed to benefit your dog’s health using all-natural organically grown herbs with no additives or preservatives.
Even if your pet is healthy, supplying a multivitamin is essential to maintain good health, and some pets need more vitamins and minerals than others. For more, read NHV’s blog, vet talk with Dr. Hillary Cook.
Benefits of NHV’s Multivitamins for Dogs
You can read NHV's blog about the importance of dog vitamin supplements. All pets can benefit from NHV’s Natural Pet Product, even small exotic pets.
If you have questions about plant-based supplements including our multivitamins for dogs, you can schedule a consultation with one of our highly trained holistic veterinarians, because, at NHV, total health and wellness for all pets is our top priority.
Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
To be taken twice daily. Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. This is the minimum dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb = 0.5 ml
16 - 30 lb = 1.0 ml
31 - 45 lb = 1.5 ml
46 - 60 lb = 2.0 ml
61 - 75 lb = 2.5 ml
Over 75 lb = 3.0 ml
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provide and places the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth.
Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken or yogurt or a favourite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and wellbeing of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Do not use Multi Essentials in pregnant or nursing animals. Speak to your vet before using our products. A second visit is recommended if your pet’s condition does not improve, or deteriorates after continued use of the supplements.
All information provided by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.
Millions of people take multivitamins daily to support their health, and it only makes sense our canine companions can benefit just as much. This 100% natural plant-based liquid blend can help your dog with nutritional deficiencies.
Signs of Possible Vitamin Deficiency in Dogs
NHV’s Multi-Essentials are packed with herbs that are rich in vitamins and minerals. This vet-formulated blend is designed to benefit your dog’s health using all-natural organically grown herbs with no additives or preservatives.
Even if your pet is healthy, supplying a multivitamin is essential to maintain good health, and some pets need more vitamins and minerals than others. For more, read NHV’s blog, vet talk with Dr. Hillary Cook.
Benefits of NHV’s Multivitamins for Dogs
You can read NHV's blog about the importance of dog vitamin supplements. All pets can benefit from NHV’s Natural Pet Product, even small exotic pets.
If you have questions about plant-based supplements including our multivitamins for dogs, you can schedule a consultation with one of our highly trained holistic veterinarians, because, at NHV, total health and wellness for all pets is our top priority.

Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
To be taken twice daily. Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. This is the minimum dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb = 0.5 ml
16 - 30 lb = 1.0 ml
31 - 45 lb = 1.5 ml
46 - 60 lb = 2.0 ml
61 - 75 lb = 2.5 ml
Over 75 lb = 3.0 ml
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provide and places the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth.
Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken or yogurt or a favourite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and wellbeing of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Do not use Multi Essentials in pregnant or nursing animals. Speak to your vet before using our products. A second visit is recommended if your pet’s condition does not improve, or deteriorates after continued use of the supplements.
All information provided by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.