liver support

free shipping over $100 (USA & Canada)
1-877-937-4372 the pet expert hotline
Hyperthyroidism in cats can affect well-being and health in a variety of ways. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding treatment and support options is imperative to the cat’s longterm health.
Hyperthyroidism is one of the most common endocrine disorders in elderly cats, where the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. This overproduction can lead to a host of health issues. The thyroid gland, located in the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating your cat’s metabolism. When it goes into overdrive, it speeds up the body’s processes, which can be quite taxing on your kitty.
The exact cause of hyperthyroidism in cats is still a bit of a mystery, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development. Most commonly, it’s due to a benign tumor on the thyroid gland, called an adenoma. Other potential risk factors include:
• Age: Older cats are more susceptible.
• Diet: Certain commercial cat foods might contain chemicals or excessive iodine that could affect thyroid health.
• Environmental factors: Exposure to certain chemicals and pollutants may also play a role.
Recognizing the symptoms early can make a significant difference in managing hyperthyroidism in cats. Here are some signs to watch for:
• Weight loss despite a ravenous appetite
• Increased appetite (polyphagia)
• Hyperactivity or restlessness
• Increased thirst (polydipsia) and urination (polyuria)
• Vomiting and diarrhea
• Poor coat condition
• Elevated heart rate (tachycardia)
• Aggression or behavioral changes
If your cat is showing any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult with your veterinarian.

Diagnosing hyperthyroidism typically involves a combination of physical exams and laboratory tests. Your vet will likely start with a thorough physical examination and may recommend the following tests:
• Blood tests: These measure the levels of thyroid hormones (T4) in the bloodstream.
• Imaging: In some cases, ultrasound or scintigraphy may be used to examine the thyroid gland more closely.
There are several effective treatment options for hyperthyroidism in cats, and the best choice depends on your cat’s overall health, age, and specific needs:
• Medications: Anti-thyroid drugs like methimazole can help manage hormone levels.
• Surgery: Thyroidectomy, or surgical removal of the thyroid gland, can be a permanent solution.
• Radioactive iodine therapy: This treatment involves a single injection that destroys overactive thyroid tissue.
• Dietary changes: Specially formulated low-iodine diets can help manage the condition.
Supplements can play a supportive role in managing hyperthyroidism. Here are a couple of recommendations:
• NHV’s Resthyro: This natural supplement supports thyroid health and helps manage the symptoms of hyperthyroidism. Always consult your veterinarian before starting any new supplement to ensure it’s appropriate for your cat’s specific condition.
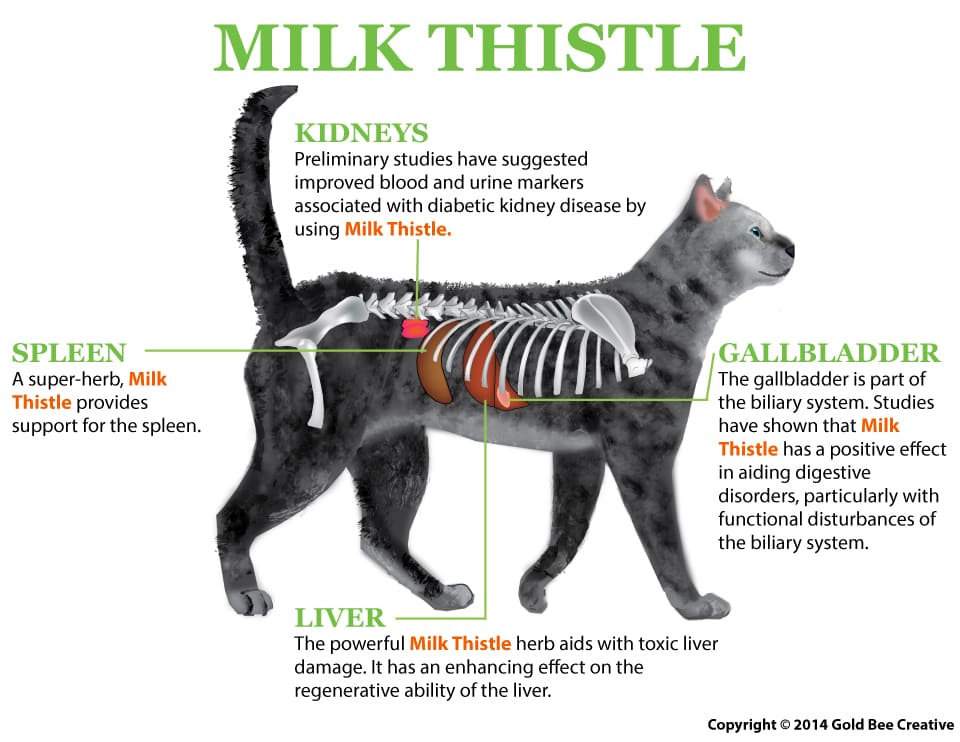
• NHV’s Milk Thistle: The medications used for hyperthyroidism can sometimes affect the liver. Milk Thistle is a fantastic supplement that supports liver health and helps in detoxifying and protecting liver function.
Diet is a crucial aspect of managing hyperthyroidism in cats. A specialized diet for hyperthyroid cats can help regulate hormone levels and support overall health. These diets typically have controlled iodine levels and balanced nutrients to support your cat’s metabolism and reduce strain on their system. NHV offers a personalized pet diet plan that can help you meet your cat’s needs.
Managing hyperthyroidism in cats can be challenging, but with the right treatment and support, your feline friend can continue to live a happy and healthy life. Regular veterinary check-ups, proper diet, and supportive supplements like Resthyro can make a world of difference.
If you suspect your cat might be suffering from hyperthyroidism, don’t hesitate to reach out to your veterinarian. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing this condition effectively. Stay informed and proactive in your cat’s health journey, and together, we can ensure our furry companions enjoy their best lives.
liver support

100% Natural Liver and Kidney Detox and Cancer Support in Cats
buy 2 and save $3
3 month supply for a small to medium size pet
What Is It?
Milk Thistle is a well-known herb among conventional and holistic veterinarians, often recommended for cats who have liver disorders, are fighting cancer, diabetes, kidney issues, gallbladder and bile duct issues, as well as hyperthyroidism.
How Does it Work?
Why Should I Trust It?
100% natural supplement approved and formulated by vets.


What Is It?
Milk Thistle is a well-known herb among conventional and holistic veterinarians, often recommended for cats who have liver disorders, are fighting cancer, diabetes, kidney issues, gallbladder and bile duct issues, as well as hyperthyroidism.
How Does it Work?
Why Should I Trust It?
100% natural supplement approved and formulated by vets.

Milk thistle, also known as Silybum Marianum is an herb that has been used for thousands of years by humans for its powerful medicinal properties. The active ingredient is Silymarin which contains flavonoids that have many beneficial properties including:
Milk thistle is one of the few herbs that have no equivalent in conventional medicine and has many uses. You can read about the many applications of Milk Thistle for cats and dogs on Dr. Hillary Cook's blog.
Milk Thistle for Liver Function
Milk Thistle for cats with liver disease is glycerin-based and safe for long-term use. This potent herbal formula provides excellent proactive support and can be taken in conjunction with conventional treatment.
Milk Thistle for Kidney Function
Milk Thistle for Anti-Cancer Support
Milk Thistle may also be beneficial to cats undergoing chemotherapy as Silymarium may enhance the activity of certain chemo drugs.
You can read Peachez's Story with Milk Thistle for cats and how it helped her with cancer and liver problems.
NHV’s certified organic Milk Thistle is a safe herb that is recommended and used by holistic practitioners. All of our products are all-natural and formulated by veterinarians with a focus on comprehensively supporting the health and well-being of your feline family member.
If you have questions about Milk Thistle or any of our plant-based products, ask an NHV expert because at NHV we want your kitty’s health to be purrfect!
NHV’s Milk Thistle for Cats contains just one ingredient.
Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
To be taken twice daily. Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. This is the minimum dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb = 0.5 ml
16 - 30 lb = 1.0 ml
31 - 45 lb = 1.5 ml
46 - 60 lb = 2.0 ml
61 - 75 lb = 2.5 ml
Over 75 lb = 3.0 ml
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provide and places the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth.
Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken or yogurt or a favorite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and wellbeing of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Do not use Milk Thistle in pregnant or nursing animals. Speak to your vet before using our products. A second visit is recommended if your pet’s condition does not improve, or deteriorates after continued use of the supplements.
All information provided by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.
Milk thistle, also known as Silybum Marianum is an herb that has been used for thousands of years by humans for its powerful medicinal properties. The active ingredient is Silymarin which contains flavonoids that have many beneficial properties including:
Milk thistle is one of the few herbs that have no equivalent in conventional medicine and has many uses. You can read about the many applications of Milk Thistle for cats and dogs on Dr. Hillary Cook's blog.
Milk Thistle for Liver Function
Milk Thistle for cats with liver disease is glycerin-based and safe for long-term use. This potent herbal formula provides excellent proactive support and can be taken in conjunction with conventional treatment.
Milk Thistle for Kidney Function
Milk Thistle for Anti-Cancer Support
Milk Thistle may also be beneficial to cats undergoing chemotherapy as Silymarium may enhance the activity of certain chemo drugs.
You can read Peachez's Story with Milk Thistle for cats and how it helped her with cancer and liver problems.
NHV’s certified organic Milk Thistle is a safe herb that is recommended and used by holistic practitioners. All of our products are all-natural and formulated by veterinarians with a focus on comprehensively supporting the health and well-being of your feline family member.
If you have questions about Milk Thistle or any of our plant-based products, ask an NHV expert because at NHV we want your kitty’s health to be purrfect!

NHV’s Milk Thistle for Cats contains just one ingredient.
Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
To be taken twice daily. Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. This is the minimum dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb = 0.5 ml
16 - 30 lb = 1.0 ml
31 - 45 lb = 1.5 ml
46 - 60 lb = 2.0 ml
61 - 75 lb = 2.5 ml
Over 75 lb = 3.0 ml
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provide and places the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth.
Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken or yogurt or a favorite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and wellbeing of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Do not use Milk Thistle in pregnant or nursing animals. Speak to your vet before using our products. A second visit is recommended if your pet’s condition does not improve, or deteriorates after continued use of the supplements.
All information provided by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.
hyperthyroidism support

Support for Hyperthyroidism in Cats
buy 2 and save $3
3 month supply for a small to medium size
What is it?
A vet-formulated feline hyperthyroidism remedy designed to help balance thyroid function, as well as manage secondary feline hyperthyroidism symptoms.
How does it work?
Why trust it?
NHV Resthyro has helped cats around the world, like Penny, who has hyperthyroidism.


What is it?
A vet-formulated feline hyperthyroidism remedy designed to help balance thyroid function, as well as manage secondary feline hyperthyroidism symptoms.
How does it work?
Why trust it?
NHV Resthyro has helped cats around the world, like Penny, who has hyperthyroidism.

NHV Resthyro™ feline hyperthyroidism remedy is made with quality herbs that are formulated to work together to support the balance of your cat’s thyroid function, support the organs affected by hyperthyroidism, and support feline hyperthyroidism symptoms. This formula has helped to support feline hyperthyroidism, for thousands of pets across the world!
Resthyro™ was formulated by a holistic veterinarian and a master herbalist with a combined 50 years of experience treating pets. It’s made using powerful herbs such as eleuthero, bugleweed, lemon balm, and gotu kola. Together, these and other ingredients help to balance thyroid hormones in your pet’s body. They help your pet’s blood pressure healthier and promote better management of stress. As a feline hyperthyroidism remedy, this supplement can be taken alongside your vet’s prescribed medication to provide comprehensive support.
Hyperthyroidism in cats is caused by excess production of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). One of the most common causes of feline hyperthyroidism is a hormone-producing benign tumor. Most cases of cats with hyperthyroidism are older pets (generally over 10 years of age).
Cats with symptoms of feline hyperthyroidism may also experience secondary problems such as mild liver, kidney, or heart disease.
NHV supplements include multiple all-natural remedies for feline hyperthyroidism. If your cat is experiencing liver problems, we suggest NHV Milk Thistle; for kidney issues, we suggest NHV Tripsy; and for heart conditions, we suggest combining NHV Hearty Heart with Resthyro™.
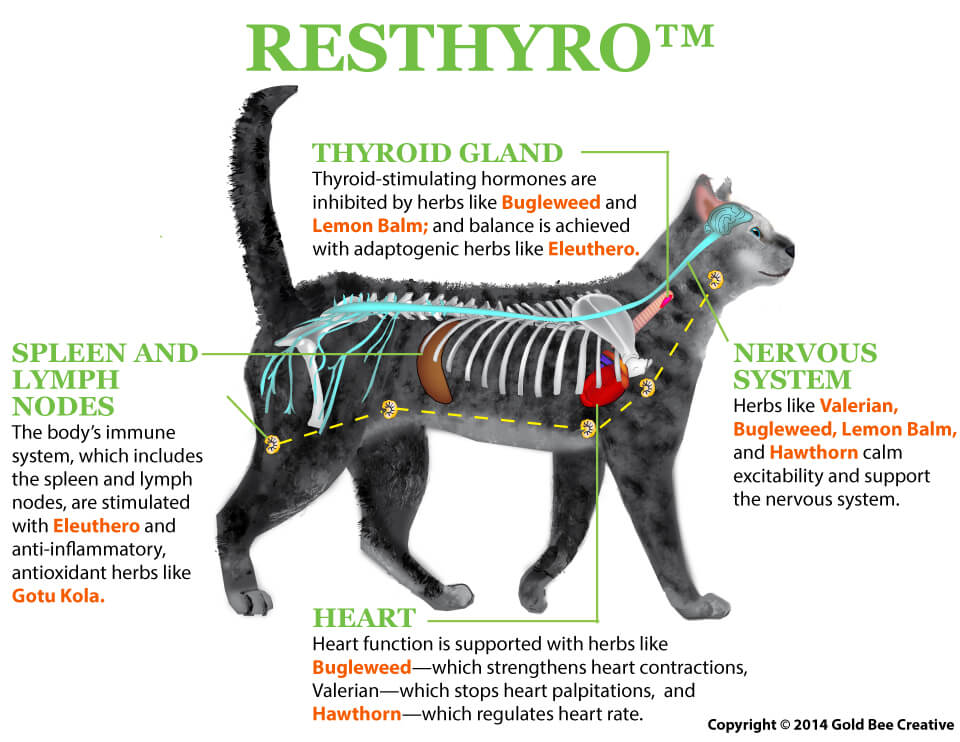
Eleuthero – Helps to balance the thyroid, stimulates the immune system, and helps to improve resistance to stress.
Bugleweed – Helps to reduce thyroid hormones in the body. It also slows and strengthens heart contractions. Relieves tension and irritability, and acts as a cough suppressant.
Lemon Balm – Inhibits thyroid activity by blocking thyroid-stimulating hormones. Also found to reduce stress, decrease blood pressure, and improve gastrointestinal activity.
Gotu Kola – A small green herb known for its cleansing abilities and used to treat skin problems. It also has strong antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Hawthorn – Helps strengthen and improve heart function.
Skullcap – Known for its relaxing and detoxifying qualities, as well as its ability to stimulate kidney function.
Valerian – Well known for its use in the treatment of anxiety, and has been used extensively as a mild sedative and pain reliever.
Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
To be taken twice daily. Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. This is the minimum dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb = 0.5 ml
16 - 30 lb = 1.0 ml
31 - 45 lb = 1.5 ml
46 - 60 lb = 2.0 ml
61 - 75 lb = 2.5 ml
Over 75 lb = 3.0 ml
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provided and place the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth.
Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken or yogurt or a favourite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and well-being of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Do not use Resthyro™ in pregnant or nursing animals. Should not be used in animals with hypothyroidism (under active thyroid gland). Speak to your vet before using our products. A second visit is recommended if your pet’s condition does not improve, or deteriorates after continued use of the supplements.
All information provided by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.
NHV Resthyro™ feline hyperthyroidism remedy is made with quality herbs that are formulated to work together to support the balance of your cat’s thyroid function, support the organs affected by hyperthyroidism, and support feline hyperthyroidism symptoms. This formula has helped to support feline hyperthyroidism, for thousands of pets across the world!
Resthyro™ was formulated by a holistic veterinarian and a master herbalist with a combined 50 years of experience treating pets. It’s made using powerful herbs such as eleuthero, bugleweed, lemon balm, and gotu kola. Together, these and other ingredients help to balance thyroid hormones in your pet’s body. They help your pet’s blood pressure healthier and promote better management of stress. As a feline hyperthyroidism remedy, this supplement can be taken alongside your vet’s prescribed medication to provide comprehensive support.
Hyperthyroidism in cats is caused by excess production of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). One of the most common causes of feline hyperthyroidism is a hormone-producing benign tumor. Most cases of cats with hyperthyroidism are older pets (generally over 10 years of age).
Cats with symptoms of feline hyperthyroidism may also experience secondary problems such as mild liver, kidney, or heart disease.
NHV supplements include multiple all-natural remedies for feline hyperthyroidism. If your cat is experiencing liver problems, we suggest NHV Milk Thistle; for kidney issues, we suggest NHV Tripsy; and for heart conditions, we suggest combining NHV Hearty Heart with Resthyro™.

Eleuthero – Helps to balance the thyroid, stimulates the immune system, and helps to improve resistance to stress.
Bugleweed – Helps to reduce thyroid hormones in the body. It also slows and strengthens heart contractions. Relieves tension and irritability, and acts as a cough suppressant.
Lemon Balm – Inhibits thyroid activity by blocking thyroid-stimulating hormones. Also found to reduce stress, decrease blood pressure, and improve gastrointestinal activity.
Gotu Kola – A small green herb known for its cleansing abilities and used to treat skin problems. It also has strong antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Hawthorn – Helps strengthen and improve heart function.
Skullcap – Known for its relaxing and detoxifying qualities, as well as its ability to stimulate kidney function.
Valerian – Well known for its use in the treatment of anxiety, and has been used extensively as a mild sedative and pain reliever.
Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
To be taken twice daily. Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. This is the minimum dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb = 0.5 ml
16 - 30 lb = 1.0 ml
31 - 45 lb = 1.5 ml
46 - 60 lb = 2.0 ml
61 - 75 lb = 2.5 ml
Over 75 lb = 3.0 ml
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provided and place the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth.
Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken or yogurt or a favourite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and well-being of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Do not use Resthyro™ in pregnant or nursing animals. Should not be used in animals with hypothyroidism (under active thyroid gland). Speak to your vet before using our products. A second visit is recommended if your pet’s condition does not improve, or deteriorates after continued use of the supplements.
All information provided by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.
hyperthyroidism support

Natural Support for Hyperthyroidism in Cats & Pets
bundle and save with pet expert kits
3 month supply for a small to medium size pet
What is it?
A complete kit to support your pet through symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
How Does it Work?
Why Should I Trust It?
Safe to use long-term, vet-formulated, and vet-approved.


What is it?
A complete kit to support your pet through symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
How Does it Work?
Why Should I Trust It?
Safe to use long-term, vet-formulated, and vet-approved.

This supplement has been formulated combining several different herbs that are known to help control thyroid hormone production, and support heart circulatory and kidney function.
When using supplements to support hyperthyroidism it is important that the organs most affected by the condition are supported as well. Turmeric contains curcumin, which is a powerful antioxidant that makes it beneficial for discomfort and inflammation. Research has found that it is a powerful herb for heart health. It helps with hypertension, lowers bad cholesterol and supports both the heart and liver function. It is also beneficial in aiding digestion and diarrhea in cats and dogs.
Natural Support and can be used in conjunction with Vet-Prescribed Treatment of Hyperthyroidism in Cats
Hyperthyroidism is a common condition seen in middle-aged to older cats. This condition is exceedingly rare in dogs. Hyperthyroidism is caused when there is an overproduction of thyroid hormones T3 and T4. As the thyroid hormones control the function of nearly all the organs, it is common to see secondary health conditions such as heart disease, hypertension, and kidney disease.
With NHV’s Hyperthyroidism Gold Support Kit, you will get an effective blend of herbs that are safe to use long-term and are vet-recommended natural treatments for hyperthyroidism in cats. Find out how Penny improved her quality of life with NHV’s plant-based products.
Read more about hyperthyroidism medicine for cats on our blog at Vet Talk with Dr. Hillary Cook, because at NHV we want to support pet parents to help their fur babies in every way possible.
NHV’s Hyperthyroidism Gold Support Kit contains two potent blends of vet-formulated herbal supplements that may help support your cat’s thyroid as well as the overall function of the thyroid gland.
1.NHV’s Resthyro — A powerful blend of herbs that help control thyroid function as well as supporting heart circulation and kidney function make this a great additional support as well as being a vet-recommended natural support for hyperthyroidism in cats.
2.NHV’s Turmeric — A potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory that contains curcumin, which is highly effective for discomfort and inflammation. This herb also aids in
Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
To be taken twice daily. Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. This is the minimum dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb = 0.5 ml
16 - 30 lb = 1.0 ml
31 - 45 lb = 1.5 ml
46 - 60 lb = 2.0 ml
61 - 75 lb = 2.5 ml
Over 75 lb = 3.0 ml
For small animals (rabbits, ferrets), avians and reptiles use 1 drop for every 2 lb of body weight.
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provided and place the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth. Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken or yogurt or a favorite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and well-being of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Do not use in pregnant or nursing animals.
All information provided by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.
This supplement has been formulated combining several different herbs that are known to help control thyroid hormone production, and support heart circulatory and kidney function.
When using supplements to support hyperthyroidism it is important that the organs most affected by the condition are supported as well. Turmeric contains curcumin, which is a powerful antioxidant that makes it beneficial for discomfort and inflammation. Research has found that it is a powerful herb for heart health. It helps with hypertension, lowers bad cholesterol and supports both the heart and liver function. It is also beneficial in aiding digestion and diarrhea in cats and dogs.
Natural Support and can be used in conjunction with Vet-Prescribed Treatment of Hyperthyroidism in Cats
Hyperthyroidism is a common condition seen in middle-aged to older cats. This condition is exceedingly rare in dogs. Hyperthyroidism is caused when there is an overproduction of thyroid hormones T3 and T4. As the thyroid hormones control the function of nearly all the organs, it is common to see secondary health conditions such as heart disease, hypertension, and kidney disease.
With NHV’s Hyperthyroidism Gold Support Kit, you will get an effective blend of herbs that are safe to use long-term and are vet-recommended natural treatments for hyperthyroidism in cats. Find out how Penny improved her quality of life with NHV’s plant-based products.
Read more about hyperthyroidism medicine for cats on our blog at Vet Talk with Dr. Hillary Cook, because at NHV we want to support pet parents to help their fur babies in every way possible.
NHV’s Hyperthyroidism Gold Support Kit contains two potent blends of vet-formulated herbal supplements that may help support your cat’s thyroid as well as the overall function of the thyroid gland.
1.NHV’s Resthyro — A powerful blend of herbs that help control thyroid function as well as supporting heart circulation and kidney function make this a great additional support as well as being a vet-recommended natural support for hyperthyroidism in cats.
2.NHV’s Turmeric — A potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory that contains curcumin, which is highly effective for discomfort and inflammation. This herb also aids in
Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
To be taken twice daily. Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. This is the minimum dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb = 0.5 ml
16 - 30 lb = 1.0 ml
31 - 45 lb = 1.5 ml
46 - 60 lb = 2.0 ml
61 - 75 lb = 2.5 ml
Over 75 lb = 3.0 ml
For small animals (rabbits, ferrets), avians and reptiles use 1 drop for every 2 lb of body weight.
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provided and place the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth. Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken or yogurt or a favorite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and well-being of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Do not use in pregnant or nursing animals.
All information provided by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.