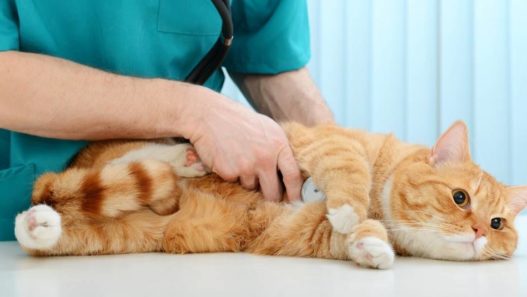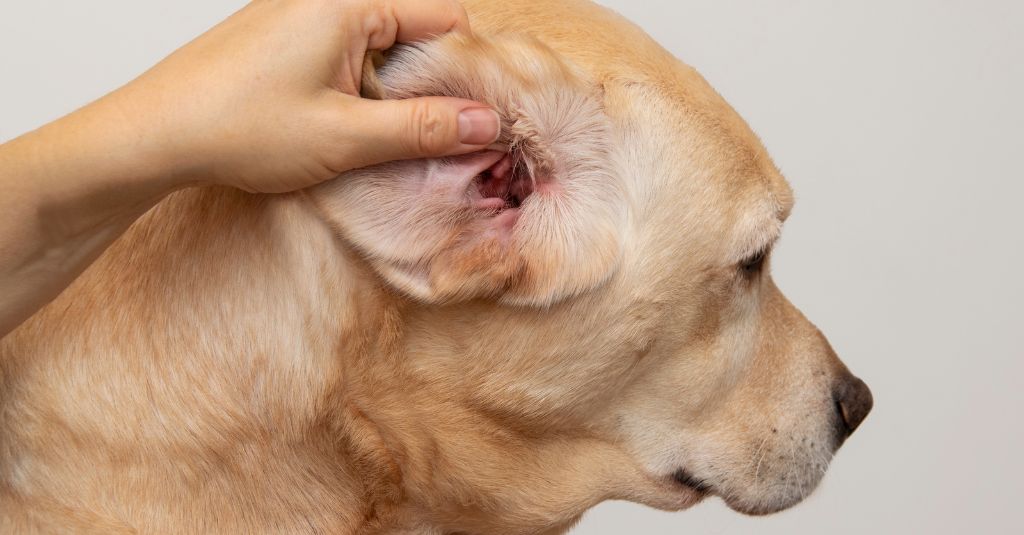
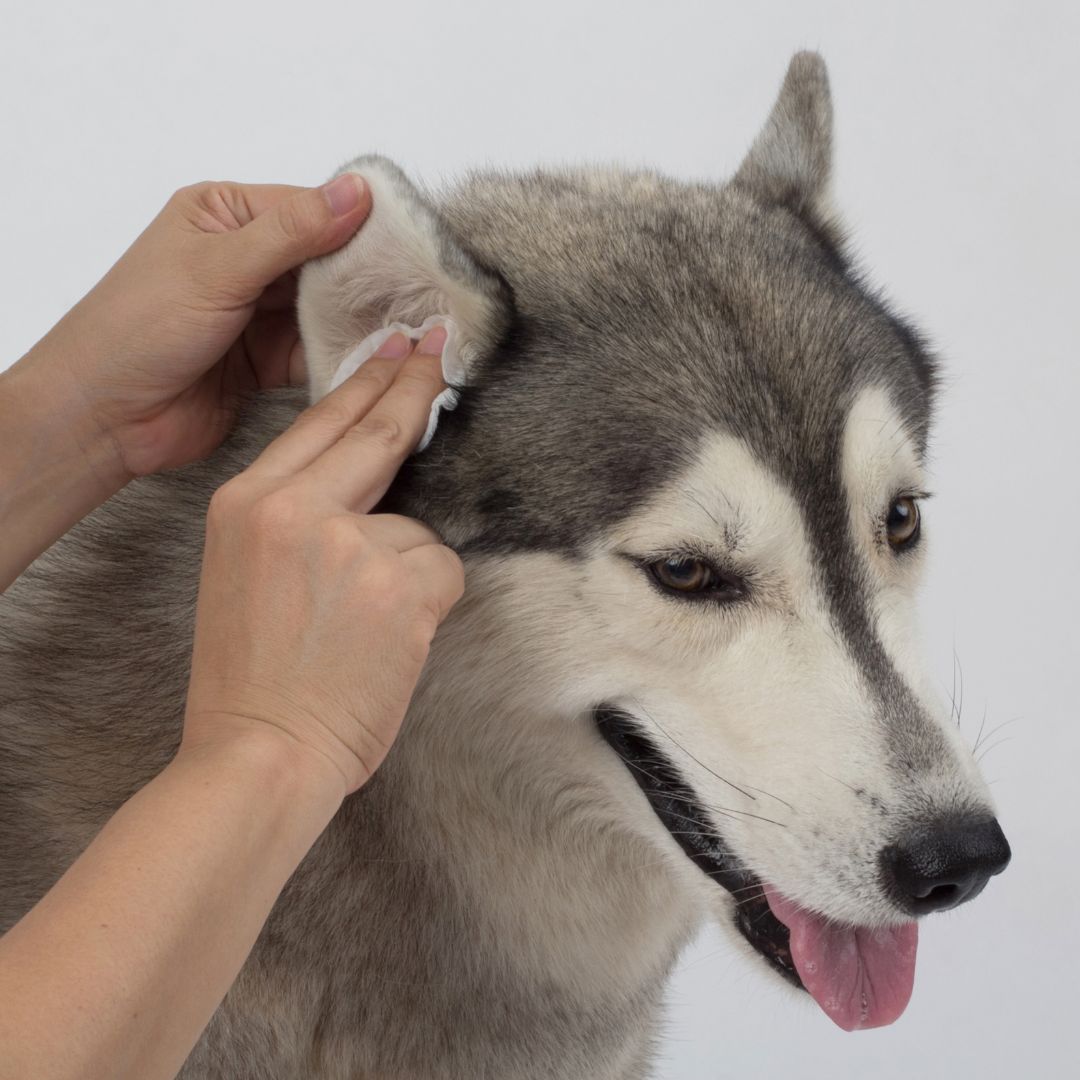
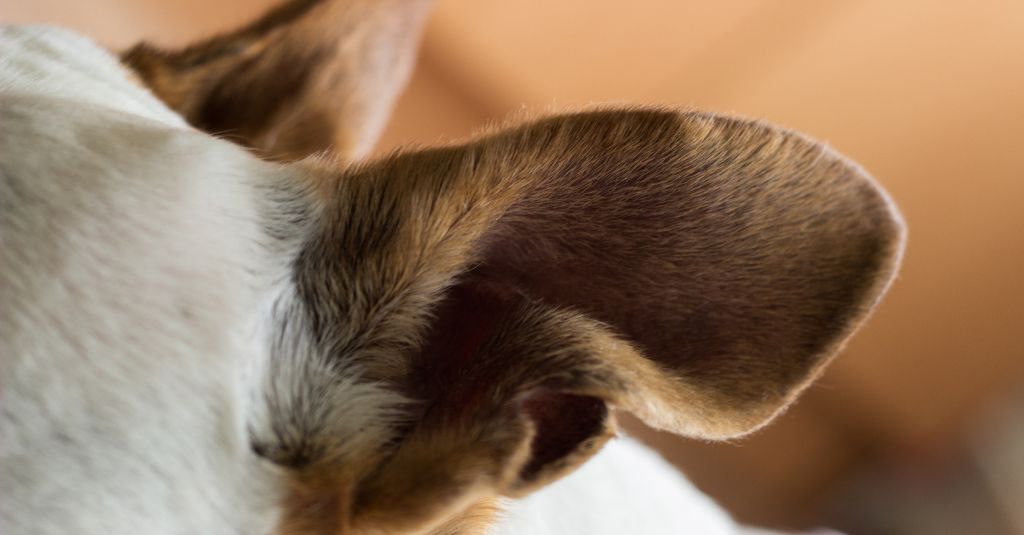
Ear hematomas, also known as aural hematomas, are a common and often painful condition that affects pets, particularly dogs and less frequently cats.
What is an Ear Hematoma in Pets and How Does It Develop?
An ear hematoma is a collection of blood that accumulates within the cartilage of the ear and the skin. This condition occurs when blood vessels in the ear flap rupture, leading to blood pooling between the skin and cartilage of the pinna (the visible part of the outer ear that collects sound waves and directs them into the ear canal).
Ear hematomas are more common in dogs than in cats and are often associated with trauma or underlying ear infections.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary causes of ear hematomas in pets include:
- Trauma: Vigorous head shaking or scratching, often due to underlying ear conditions such as otitis externa or media, can lead to the rupture of blood vessels in the ear flap.
- Breed predisposition: Dogs with certain ear conformations, such as V-shaped or semi-erect ears, are more prone to developing aural hematomas due to mechanical trauma along the cartilage folds.
- Immunological factors: Some studies suggest that underlying immune-mediated processes may contribute to the development of ear hematomas in certain cases.
- Age and size: Epidemiological studies have shown that older dogs and those of medium to large size have a higher prevalence of ear hematomas.
- Ear structure: Dogs with pendulous ears are more frequently affected by aural hematomas.
- Gender: Male dogs have shown a higher prevalence of this condition.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of ear hematomas can vary between dogs and cats:
In Dogs
- A soft, fluid-filled swelling on the concave surface of the ear flap
- Swelling that may vary in size and potentially occlude the ear canal
- Head shaking and ear scratching
- Warm and soft swelling in the early stages
- Potential development of a “cauliflower” ear if left untreated
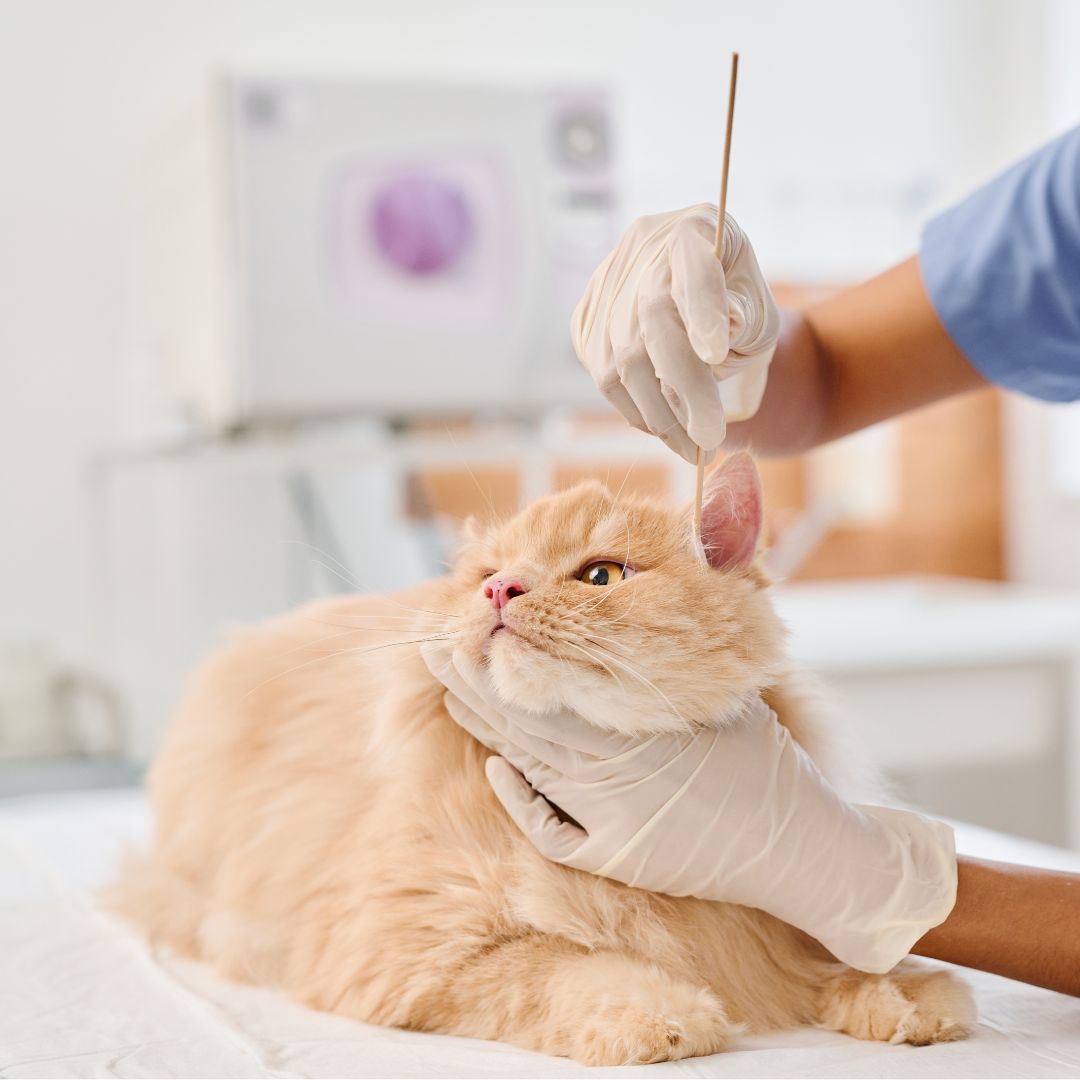
In Cats
- Similar presentation to dogs, but with notable differences due to the sensitivity of feline ear cartilage
- Higher risk of severe inflammation
- Potential for a permanently narrowed ear canal and increased risk of long-term ear infections
- More pronounced deformities, such as curling and softening of the ear flap
It is important to note that cats are more prone to severe inflammation compared to dogs, making early intervention crucial to preserve ear function and prevent long-term complications.
Seeking Professional Care
When it comes to ear hematomas in pets, seeking prompt veterinary care is essential. Aural hematomas can cause significant discomfort and pain to the pet. Delaying treatment can lead to complications such as permanent ear deformity, often referred to as “cauliflower ear.”
As ear hematomas are often associated with underlying conditions such as ear infections, allergies, or trauma, professional evaluation is necessary to diagnose and treat any concurrent conditions effectively, preventing recurrence and further complications.
Treatment options vary based on the severity of the hematoma
Veterinarians use a combination of physical examinations and diagnostic tests, such as fine needle aspiration, to confirm the presence of a hematoma and rule out other conditions. Treatment options vary based on the severity of the hematoma and may include surgical intervention, aspiration, or corticosteroid injections.
If left untreated, aural hematomas can lead to chronic inflammation, scarring, and potential obstruction of the ear canal, which can impair hearing and lead to further infections.
While some home remedies may provide temporary relief, they are not substitutes for professional veterinary care. Veterinary intervention is necessary to ensure proper drainage and healing, and to prevent the hematoma from refilling.
By seeking professional care promptly, pet owners can ensure proper diagnosis, treatment, and management of any underlying conditions, promoting better recovery outcomes for their pets.

Treatment Options for Ear Hematoma in Pets
Treatment of an aural hematoma often requires addressing the underlying cause
The treatment of ear hematomas in pets involves a range of options, from traditional approaches, such as corticosteroid therapy, drainage and placement of drains to emerging therapies and holist support. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the size and severity of the hematoma, the overall health of the pet, and the veterinarian’s assessment.
Emerging treatment options can include Platelet-rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy and advanced surgical techniques for example.
It is crucial to note that successful treatment of an aural hematoma often requires addressing the underlying cause, such as ear infections, allergies, or foreign bodies, to prevent recurrence. Veterinary consultation is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment based on the specific circumstances of each case.
Home Care and Recovery Support
While professional veterinary care is crucial for treating ear hematomas, several evidence-based home care techniques can support recovery and provide relief for pets. These techniques should be used in conjunction with, not as a replacement for, professional veterinary treatment.
1. Warm Compresses
Applying a warm compress to the affected ear can help reduce swelling and promote better blood circulation. This technique involves gently applying a clean cloth soaked in warm water to the ear daily. The warmth helps in soothing the area and may assist in the reabsorption of the hematoma.
2. Preventing Further Trauma
Preventing the pet from scratching or shaking its head is crucial to avoid exacerbating the condition. Using an Elizabethan collar (e-collar) can prevent the pet from causing further damage to the ear. Additionally, trimming the pet’s nails can reduce the risk of injury from scratching.
3. Monitoring and Rest
Ensuring that the pet rests and avoids activities that could worsen the hematoma is important. Monitoring the pet for any signs of discomfort or changes in the condition of the ear is also essential. This includes watching for increased swelling, redness, or signs of infection.
4. Natural Supplements and Remedies
In addition to conventional treatments, certain supplements and natural remedies may support recovery and reduce inflammation in pets with ear hematomas.
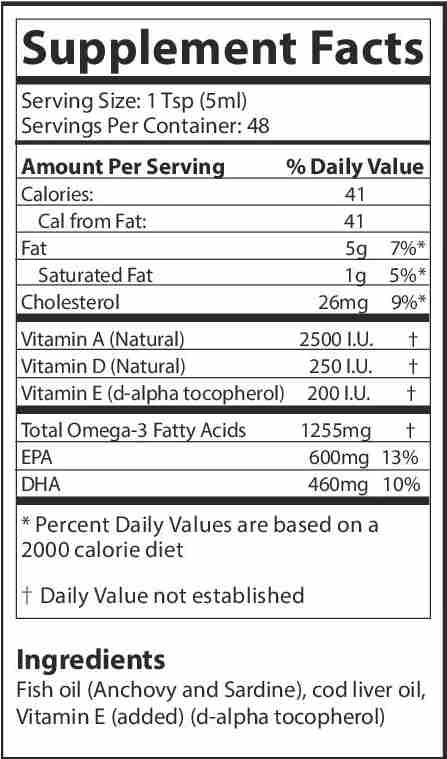
- NHV PetOmega-3 is rich in omega-3 fatty acids and has anti-inflammatory properties that may support recovery. It also promotes skin and coat health.
- NHV Turmeric is a potent anti-inflammatory that may help with inflammation and discomfort.
- NHV Stimmune aids in balancing the immune system, contributing preventatively to immune-mediated issues.
- NHV Echo Gold Reduces inflammation in the ear canal; aids in eliminating ear mites and triggers that cause infection. In addition, alleviates itching and scratching, and helps eliminate canine ear discharge supporting the reduction of unpleasant odors.
5. Compression Wraps
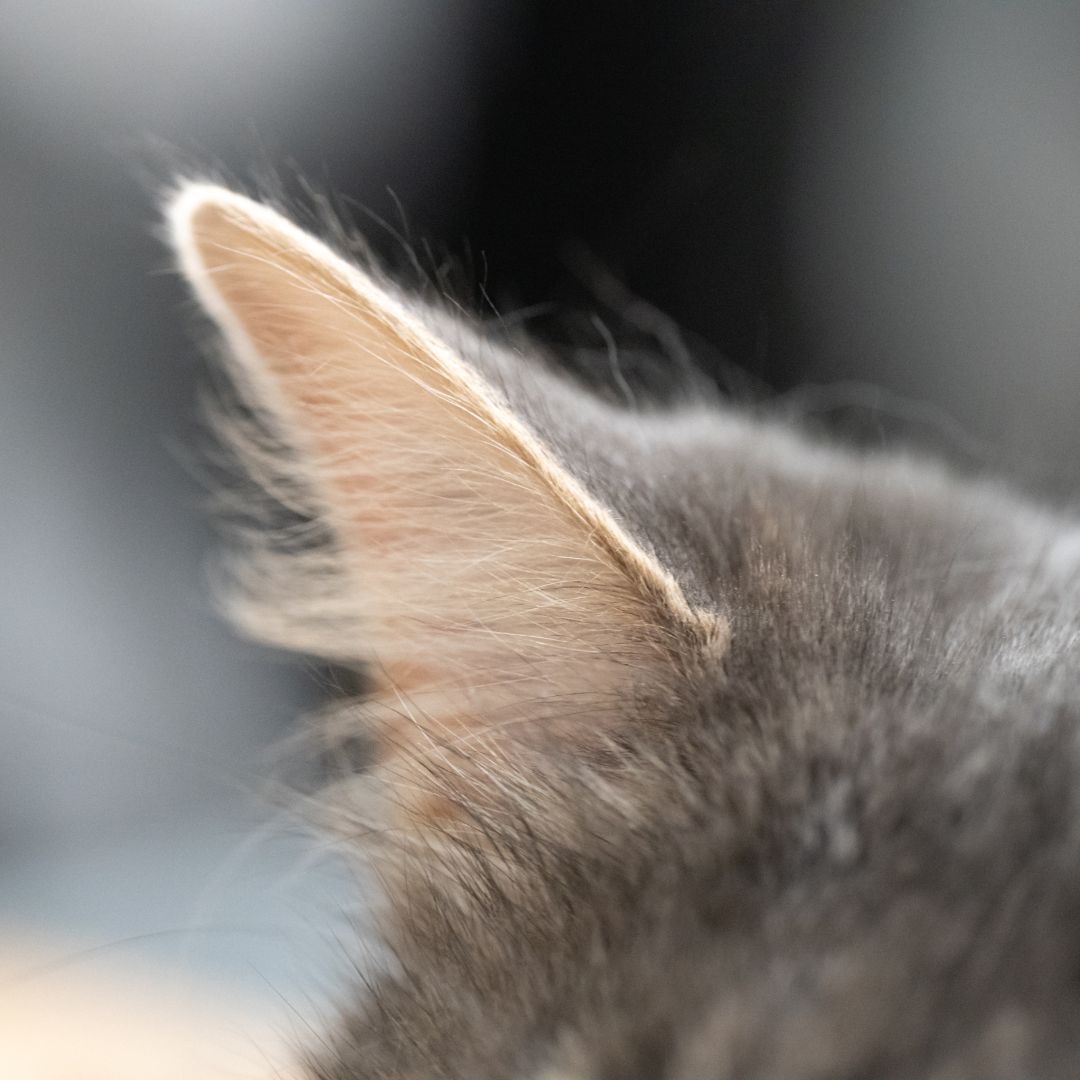

While not a supplement or remedy, using compression wraps can help manage an ear hematoma by keeping the ear snugly against the dog’s head, limiting head shaking and further trauma. This can help reduce swelling and encourage quicker reabsorption of blood.
It is important to note that while these supplements and natural remedies can be part of a holistic approach to managing ear hematomas in pets, they should be used under veterinary guidance and in conjunction with professional treatment.
Conclusion
With proper care and attention, most pets can recover successfully
Ear hematomas in pets are a challenging condition that requires prompt attention and comprehensive care. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking timely veterinary intervention, pet owners can play a crucial role in their pet’s recovery. The combination of professional treatment, appropriate home care, and preventive measures can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Remember that each pet’s situation is unique, and what works for one may not be suitable for another. Always consult with a veterinarian to develop a tailored treatment and recovery plan for your pet. With proper care and attention, most pets can recover successfully from ear hematomas and return to their happy, healthy lives.

Turmeric
Turmeric - A supper food that is beneficial for over all wellbeing

Turmeric - A supper food that is beneficial for over all wellbeing
- item number
- ph8100fb
- weight
- 0.7
-
Description
- item number
- ph8100fb
- weight
- 0.7
-
Ingredients
-
Dosage
ear health

Echo Gold for dogs
Echo Gold for dogs
Holistic Ear Drops for Dogs
buy 2 and save $3
What is it?
NHV Echo Gold is a vet-formulated ear drops for dogs. It is designed to help ease discomfort and inflammation caused by dog ear mites, allergens, insect bites, parasitic mites, fungal/bacterial dog ear infection, and more.
How Does it Work?
- Helps soothe the swollen dog ear canal and outer ear caused by dog ear infection
- Promotes speedy healing of dog ear infection
- Helps your pup cope with the uncomfortable symptoms ear conditions may cause.
- Helps reduce ear odor, itching and scratching
Why Should I Trust It?
100% natural and topical use only.


What is it?
NHV Echo Gold is a vet-formulated ear drops for dogs. It is designed to help ease discomfort and inflammation caused by dog ear mites, allergens, insect bites, parasitic mites, fungal/bacterial dog ear infection, and more.
How Does it Work?
- Helps soothe the swollen dog ear canal and outer ear caused by dog ear infection
- Promotes speedy healing of dog ear infection
- Helps your pup cope with the uncomfortable symptoms ear conditions may cause.
- Helps reduce ear odor, itching and scratching
Why Should I Trust It?
100% natural and topical use only.

Has your pup been shaking his/her head a lot? This could be caused by dog ear infection!
Seeing our precious little ones suffering from dog ear infection is not easy. However, this condition is extremely common in dogs, which begs the question - how can we help support them? The herbal ear drops for dogs, Echo Gold, can help with ear infection symptoms and healing.
Please note that this supplement can only be used topically. Warm the formula by placing the bottle in hot water or running it under hot water for 30 seconds. Shake well, then drop a few drops into the dog’s ear canal. By using a cotton swab, apply the extract to the outer ear area as well. Use twice daily to help with dog ear infection. For proactive support and regular maintenance, use as much as you need.
How NHV’s Ear Drops for Dogs Support Ear Disorders
Exterior ear canal infection is the most common ear condition in dogs. It causes excessive ear discharge, unpleasant odor, ear inflammation, and more. You may also notice your pup shaking, scratching and rubbing their head frequently due to pain and itchiness. Echo Gold for Dogs can help address these uncomfortable symptoms.
This herbal formula possesses anti-inflammatory and antibiotic properties. The blend of herbs - chamomile, Goldenseal, Echinacea angustifolia, Myrrh, and tea tree oil - helps support your furkid’s ear condition in different ways.
Herbs like Echinacea angustifolia, Myrrh, and Tea tree oil are traditionally used to manage infections. Their anti-microbial and antiseptic properties help control and inhibit bacterial formation. Tea tree oil can even help eliminate bad odors caused by ear infections.
Goldenseal and Chamomile can help soothe and heal inflamed and irritated ears. The analgesic ability of Chamomile can even help with the discomfort dog ear infection may cause.
Our Canadian-made products have supported thousands of pets worldwide! Read NHV reviews and how they’ve helped other furmilies. They are human-grade quality products made in a GMP-certified, FDA-approved facility. Your furkiddo’s health and safety are our top priorities!
Possible Causes of Dog Ear Infection
Ear infections could be a complication of an underlying disease. It is vital to pinpoint the root cause in order to cure your pup.
- Bacterial and yeast infections
- Food or environmental allergies
- Ear mites and parasites
- Hormonal imbalances (hypothyroidism)
- Breed-related issues
- Tumors
- Immune conditions
Natural Support for Dog Ear Infection
All our products are 100% natural herbal supplements formulated by a holistic veterinarian and master herbalist with over 50+ years of experience.
We have a team of supportive Pet Experts to help you and your furkiddos with any questions and concerns! So, please don’t hesitate to reach out if you need anything! We are always here to help.
Help protect your dog from ear infections by ordering our Echo Gold for dogs!
Additional Support for Dog Ear Infection and Other Ear Issues
For more information about ear infections in dogs and our Echo Drop, click to watch our video about Ear Infection Support For Cats & Dogs here. Or read our blog post on on how to prevent ear infections in cats and dogs.
In addition to herbal supplements like ear drops for dogs, regular ear cleaning is vital for recovery. Watch our YouTube videos on tips for cleaning Your pet's ears and ways to clean your little one’s ears.
- item number
- PH1750d
- weight
- 0.7
- volume
- 1 fl. oz (30ml)
- form
- liquid
- life stages
- adult, senior, puppy
- made in
- canada
All NHV supplements are made with the finest quality organic or ethically harvested herbs. We use non-GMO vegetable glycerin as our base. NHV products are full-spectrum extracts.
- Chamomile – Helps soothe and heal inflamed skin, speed healing of ear mite bites in and around the ear, and combat allergies that can trigger infections.
- Goldenseal – Has anti-inflammatory properties, which help fight dog ear infection.
- Echinacea Angustifolia – Helps strengthen the immune system and helps your pup fight infections.
- Myrrh – Studies have shown that it helps increase the white blood cell count, which will help your dog fight the infection quickly.
- Tea Tree Oil– A gentle antiseptic, beneficial for fungal (yeast) and bacterial infections.
Topical Use Only: Warm the ECHO GOLD by placing the bottle in hot water or running under hot water for 30 seconds. Shake well. Place a few drops in to the ear canal. Using a cotton swab apply to outer ear area as well.
Information presented by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.
-
Description
Has your pup been shaking his/her head a lot? This could be caused by dog ear infection!
Seeing our precious little ones suffering from dog ear infection is not easy. However, this condition is extremely common in dogs, which begs the question - how can we help support them? The herbal ear drops for dogs, Echo Gold, can help with ear infection symptoms and healing.
Please note that this supplement can only be used topically. Warm the formula by placing the bottle in hot water or running it under hot water for 30 seconds. Shake well, then drop a few drops into the dog’s ear canal. By using a cotton swab, apply the extract to the outer ear area as well. Use twice daily to help with dog ear infection. For proactive support and regular maintenance, use as much as you need.
How NHV’s Ear Drops for Dogs Support Ear Disorders
Exterior ear canal infection is the most common ear condition in dogs. It causes excessive ear discharge, unpleasant odor, ear inflammation, and more. You may also notice your pup shaking, scratching and rubbing their head frequently due to pain and itchiness. Echo Gold for Dogs can help address these uncomfortable symptoms.
This herbal formula possesses anti-inflammatory and antibiotic properties. The blend of herbs - chamomile, Goldenseal, Echinacea angustifolia, Myrrh, and tea tree oil - helps support your furkid’s ear condition in different ways.
Herbs like Echinacea angustifolia, Myrrh, and Tea tree oil are traditionally used to manage infections. Their anti-microbial and antiseptic properties help control and inhibit bacterial formation. Tea tree oil can even help eliminate bad odors caused by ear infections.
Goldenseal and Chamomile can help soothe and heal inflamed and irritated ears. The analgesic ability of Chamomile can even help with the discomfort dog ear infection may cause.
Our Canadian-made products have supported thousands of pets worldwide! Read NHV reviews and how they’ve helped other furmilies. They are human-grade quality products made in a GMP-certified, FDA-approved facility. Your furkiddo’s health and safety are our top priorities!
Possible Causes of Dog Ear Infection
Ear infections could be a complication of an underlying disease. It is vital to pinpoint the root cause in order to cure your pup.
- Bacterial and yeast infections
- Food or environmental allergies
- Ear mites and parasites
- Hormonal imbalances (hypothyroidism)
- Breed-related issues
- Tumors
- Immune conditions
Natural Support for Dog Ear Infection
All our products are 100% natural herbal supplements formulated by a holistic veterinarian and master herbalist with over 50+ years of experience.
We have a team of supportive Pet Experts to help you and your furkiddos with any questions and concerns! So, please don’t hesitate to reach out if you need anything! We are always here to help.
Help protect your dog from ear infections by ordering our Echo Gold for dogs!
Additional Support for Dog Ear Infection and Other Ear Issues
For more information about ear infections in dogs and our Echo Drop, click to watch our video about Ear Infection Support For Cats & Dogs here. Or read our blog post on on how to prevent ear infections in cats and dogs.
In addition to herbal supplements like ear drops for dogs, regular ear cleaning is vital for recovery. Watch our YouTube videos on tips for cleaning Your pet's ears and ways to clean your little one’s ears.
- item number
- PH1750d
- weight
- 0.7
- volume
- 1 fl. oz (30ml)
- form
- liquid
- life stages
- adult, senior, puppy
- made in
- canada
-
Ingredients
All NHV supplements are made with the finest quality organic or ethically harvested herbs. We use non-GMO vegetable glycerin as our base. NHV products are full-spectrum extracts.
- Chamomile – Helps soothe and heal inflamed skin, speed healing of ear mite bites in and around the ear, and combat allergies that can trigger infections.
- Goldenseal – Has anti-inflammatory properties, which help fight dog ear infection.
- Echinacea Angustifolia – Helps strengthen the immune system and helps your pup fight infections.
- Myrrh – Studies have shown that it helps increase the white blood cell count, which will help your dog fight the infection quickly.
- Tea Tree Oil– A gentle antiseptic, beneficial for fungal (yeast) and bacterial infections.
-
Dosage
Topical Use Only: Warm the ECHO GOLD by placing the bottle in hot water or running under hot water for 30 seconds. Shake well. Place a few drops in to the ear canal. Using a cotton swab apply to outer ear area as well.
Information presented by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.
ear health

Ear Infections Gold Care Kit
Ear Infections Gold Care Kit
Echo Gold & Alge-Ex
bundle and save with pet expert kits
3 month supply for a small to medium size pet.
What is it?
Our Ear Infections Gold Care Kit is designed to relieve wax buildup caused by parasitic ear mites, allergens, food allergies or a side effect from another health issue.
How Does it Work?
- Beneficial support for soothing ear infections
- Natural aid for relieving symptoms of environmental allergies
- Helps rebalance the immune system and combat infection
- May eliminate bad odors and ear discharge
Why Should I Trust It?
Vet-approved and vet-formulated natural remedies, safe for long-term use.


What is it?
Our Ear Infections Gold Care Kit is designed to relieve wax buildup caused by parasitic ear mites, allergens, food allergies or a side effect from another health issue.
How Does it Work?
- Beneficial support for soothing ear infections
- Natural aid for relieving symptoms of environmental allergies
- Helps rebalance the immune system and combat infection
- May eliminate bad odors and ear discharge
Why Should I Trust It?
Vet-approved and vet-formulated natural remedies, safe for long-term use.

If your furry friend is shaking their head, scratching or holding their head to one side, they may have an ear infection.
Natural Cat and Dog Ear Infection Remedy
Ear infections in dogs and cats are fairly common and some breeds are more susceptible because the anatomy of their ears may trap moisture and debris inside the ear. Dogs with floppy ears like the American English Coonhound or cats with smaller outer ears like Himalayans are prone to developing ear infections.
Diagnosing these conditions requires a thorough examination of your dog or cat’s ear. Once diagnosed, your vet may recommend pairing a topical remedy like Echo Gold with an oral supplement like Alge-Ex if the cause is environmental.
Potential Causes of Cat and Dog Ear Infections
- Breed related issues
- Allergies due to food or environmental irritants
- Parasites (eg. ear mites)
- Other health issues that trigger hormonal imbalance (hypothyroidism)
- Grass or moist hair (foreign particles)
- Excess wax (wax moisture promotes bacterial growth and infection)
- Bacteria and yeast infections
- Immune conditions
- Tumors
How NHV Supplements Help Prevent Ear Infections
Ear infections can cause a lot of discomfort and itchiness in your furry friend. Soothing ingredients like ginger, chamomile and myrrh provide relief as your pet recovers while ingredients like goldenseal and tea tree oil contain antibacterial and antifungal properties which help control infections in and around the ear. The immune-stimulating properties in Echo Gold and Alge-Ex increase antibody production and help control histamine response. Algae-Ex provides internal support while Echo Gold is beneficial for protecting and soothing overall ear discomfort.
ECHO GOLD
- Beneficial support for soothing inflammation in the ear
- May ease discomfort and irritated skin
- Helps eliminate ear discharge and odor
ALGE-EX
- Natural aid for restoring healthy immune response and histamine activity
- May reduce symptoms of environmental allergies like itchiness and scabby skin
- Natural support to combat bacterial and fungal (yeast) infections
Natural Support For Your Pets
If you suspect your pet has an ear infection, book an appointment with your trusted pet-care professional. Our Ear Infections Gold Care Kit helps relieve symptoms of pet ear infections and compliments vet-prescribed medications. It should not replace them. For any questions or concerns about ear health and cleaning tips, get in touch with an NHV Pet Expert.
- item number
- BD5037
- weight
- 1.4
- volume
- 3.4 fl. oz (100ml) + 1 fl. oz. (30ml)
- form
- liquid
- life stages
- adult, senior, puppy/kitten
- made in
- Canada
Made with the finest, organically grown or ethically harvested herbs. Made specifically for pets, vet-formulated and vet approved.
Echo Gold
- Chamomile is a natural aid for reducing inflammation caused by flea bites, environmental allergies and infections.
- Echinacea Angustifolia is commonly used for fighting infections because of its many immune-stimulating and antimicrobial properties.
- Goldenseal acts as an anti-inflammatory for ulcers and irritations of the ear as well as act like a natural disinfectant (antiseptic properties).
- Myrrh is a natural antiseptic with anti-inflammatory properties to relieve irritated skin and enhance healing.
- Tea Tree Oil is often used for ear infections and to eliminate bad odors. It is also helpful for infected wounds and to fight off parasitic infections.
Alge-Ex
- Echinacea Angustifolia has been shown to have immunostimulant effects. Its antimicrobial properties help the body fight off infections and flushes the lymph system, which in turn expels waste from the body.
- European Golden Rod has been used to soothe symptoms of environmental allergies and to fight fungal infections.
- Eyebright has a long history of being used for allergies, skin conditions and upper respiratory tract infections. It has demonstrated antibacterial and antifungal properties.
- Feverfew is considered to be very safe for dogs and cats and can be used as an alternative to aspirin. It is a herb that inhibits the release of histamine and serotonin.
- Ginger has been shown to have excellent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It helps combat infections and soothes discomfort (analgesic properties).
Pet's Weight Dosage
To be taken twice daily. All NHV supplements are designed to be used together, and can, therefore, be given at once for convenience.
Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
ECHO GOLD : TOPICAL USE ONLY
Topical Use Only: Warm the ECHO GOLD by placing the bottle in hot water or running under hot water for 30 seconds. Shake well. Place a few drops in to the ear canal. Using a cotton swab apply to outer ear area as well.
ALGE-EX : To be taken twice daily. Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. This is the minimum dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb = 0.5 ml
16 - 30 lb = 1.0 ml
31 - 45 lb = 1.5 ml
46 - 60 lb = 2.0 ml
61 - 75 lb = 2.5 ml
Over 75 lb = 3.0 ml
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provided and place the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth. Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken or yogurt or a favourite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and well-being of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Do not use ALGE-EX in pregnant or nursing animals, or animals that suffer from autoimmune disease. Speak to your vet before using our products. A second visit is recommended if your pet’s condition does not improve, or deteriorates after continued use of the supplements.
All information provided by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.
-
Description
If your furry friend is shaking their head, scratching or holding their head to one side, they may have an ear infection.
Natural Cat and Dog Ear Infection Remedy
Ear infections in dogs and cats are fairly common and some breeds are more susceptible because the anatomy of their ears may trap moisture and debris inside the ear. Dogs with floppy ears like the American English Coonhound or cats with smaller outer ears like Himalayans are prone to developing ear infections.
Diagnosing these conditions requires a thorough examination of your dog or cat’s ear. Once diagnosed, your vet may recommend pairing a topical remedy like Echo Gold with an oral supplement like Alge-Ex if the cause is environmental.
Potential Causes of Cat and Dog Ear Infections
- Breed related issues
- Allergies due to food or environmental irritants
- Parasites (eg. ear mites)
- Other health issues that trigger hormonal imbalance (hypothyroidism)
- Grass or moist hair (foreign particles)
- Excess wax (wax moisture promotes bacterial growth and infection)
- Bacteria and yeast infections
- Immune conditions
- Tumors
How NHV Supplements Help Prevent Ear Infections
Ear infections can cause a lot of discomfort and itchiness in your furry friend. Soothing ingredients like ginger, chamomile and myrrh provide relief as your pet recovers while ingredients like goldenseal and tea tree oil contain antibacterial and antifungal properties which help control infections in and around the ear. The immune-stimulating properties in Echo Gold and Alge-Ex increase antibody production and help control histamine response. Algae-Ex provides internal support while Echo Gold is beneficial for protecting and soothing overall ear discomfort.
ECHO GOLD
- Beneficial support for soothing inflammation in the ear
- May ease discomfort and irritated skin
- Helps eliminate ear discharge and odor
ALGE-EX
- Natural aid for restoring healthy immune response and histamine activity
- May reduce symptoms of environmental allergies like itchiness and scabby skin
- Natural support to combat bacterial and fungal (yeast) infections
Natural Support For Your Pets
If you suspect your pet has an ear infection, book an appointment with your trusted pet-care professional. Our Ear Infections Gold Care Kit helps relieve symptoms of pet ear infections and compliments vet-prescribed medications. It should not replace them. For any questions or concerns about ear health and cleaning tips, get in touch with an NHV Pet Expert.
- item number
- BD5037
- weight
- 1.4
- volume
- 3.4 fl. oz (100ml) + 1 fl. oz. (30ml)
- form
- liquid
- life stages
- adult, senior, puppy/kitten
- made in
- Canada
-
Ingredients
Made with the finest, organically grown or ethically harvested herbs. Made specifically for pets, vet-formulated and vet approved.
Echo Gold
- Chamomile is a natural aid for reducing inflammation caused by flea bites, environmental allergies and infections.
- Echinacea Angustifolia is commonly used for fighting infections because of its many immune-stimulating and antimicrobial properties.
- Goldenseal acts as an anti-inflammatory for ulcers and irritations of the ear as well as act like a natural disinfectant (antiseptic properties).
- Myrrh is a natural antiseptic with anti-inflammatory properties to relieve irritated skin and enhance healing.
- Tea Tree Oil is often used for ear infections and to eliminate bad odors. It is also helpful for infected wounds and to fight off parasitic infections.
Alge-Ex
- Echinacea Angustifolia has been shown to have immunostimulant effects. Its antimicrobial properties help the body fight off infections and flushes the lymph system, which in turn expels waste from the body.
- European Golden Rod has been used to soothe symptoms of environmental allergies and to fight fungal infections.
- Eyebright has a long history of being used for allergies, skin conditions and upper respiratory tract infections. It has demonstrated antibacterial and antifungal properties.
- Feverfew is considered to be very safe for dogs and cats and can be used as an alternative to aspirin. It is a herb that inhibits the release of histamine and serotonin.
- Ginger has been shown to have excellent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It helps combat infections and soothes discomfort (analgesic properties).
-
Dosage
Pet's Weight Dosage
To be taken twice daily. All NHV supplements are designed to be used together, and can, therefore, be given at once for convenience.
Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
ECHO GOLD : TOPICAL USE ONLY
Topical Use Only: Warm the ECHO GOLD by placing the bottle in hot water or running under hot water for 30 seconds. Shake well. Place a few drops in to the ear canal. Using a cotton swab apply to outer ear area as well.
ALGE-EX : To be taken twice daily. Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. This is the minimum dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb = 0.5 ml
16 - 30 lb = 1.0 ml
31 - 45 lb = 1.5 ml
46 - 60 lb = 2.0 ml
61 - 75 lb = 2.5 ml
Over 75 lb = 3.0 ml
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provided and place the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth. Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken or yogurt or a favourite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and well-being of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Do not use ALGE-EX in pregnant or nursing animals, or animals that suffer from autoimmune disease. Speak to your vet before using our products. A second visit is recommended if your pet’s condition does not improve, or deteriorates after continued use of the supplements.All information provided by NHV Natural Pet Products is for educational purposes only.
Published: January 17, 2025

 USD
USD
 Canadian Dollars
Canadian Dollars