medicinal mushroom blend

free shipping over $100 (USA & Canada)
1-877-937-4372 the pet expert hotline

Hemangiosarcoma in dogs is an aggressive form of cancer that grows in the blood vessels. Knowing the signs and treatment options is imperative for the dog’s long-term health outcomes.
Hemangiosarcoma is a type of cancer that starts in the blood vessels and can affect areas like the spleen, liver, or heart. Because it often doesn’t show symptoms until it’s advanced, it may be difficult to detect in its early stages. However, early intervention can give the dog better possible health outcomes.
The causes of hemangiosarcoma are not fully understood, but some factors can increase a dog’s risk. Older dogs and certain breeds, like German Shepherds, Golden Retrievers, and Labrador Retrievers, are more commonly affected. Previous injuries or environmental factors might also play a role. Awareness of the symptoms and close monitoring are crucial.
Detection of the early symptoms is crucial. Several may appear. The dog may experience weight loss despite eating a healthy amount. They may experience increased appetite, as dogs may eat more during periods of discomfort. They may be unusually restless or demonstrate bursts of energy. Weakness or lethargy may also be observed. Finally, they may develop pale gums, which can indicate internal bleeding or anemia.
Diagnosis of hemangiosarcoma may involve several diagnostic tools. Blood tests can check for anemia or other irregularities. X-rays, ultrasound, or CT scans can help find and assess tumors. Biopsy can be used to sample the tumor for observation under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment can vary based on the tumor’s location and the dog’s overall health. Options often include surgery to remove the tumor, medication including chemotherapy to manage the disease and prevent its reoccurrence, and dietary changes to support the dog’s overall health during treatment.
Supplements can be added to the dog’s care plan for additional support. Supplementation should focus on immune system, anti-inflammation, and organ support. NHV Natures Immuno may support the immune system, helping the dog’s resilience during treatment. PetOmega 3 contains fatty acids to help reduce inflammation and support overall health, which may be beneficial during cancer treatment. Finally, ES Clear may support liver health and detoxification, which can be helpful should the liver be affected.
If the dog presents any of these symptoms they will need veterinary care for diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention is key to successful outcomes. For integrative care, herbal supplements may benefit certain symptoms and concerns.
medicinal mushroom blend

Vet-Formulated Supplement of Medicinal Mushrooms for Dogs
buy 2 and save $3
3 month supply for a small to medium size pet
Natures Immuno is formulated for dogs from Turkey Tail, Cordyceps, Reishi, Shiitake, and Agaricus mushrooms by a holistic veterinarian and master herbalist. Medicinal mushrooms like these have been used for thousands of years in Chinese medicine as well as traditional herbalism. Researchers around the globe are now studying their potential in helping with cancer, balancing the immune system, and helping with digestive problems and more.


Natures Immuno is formulated for dogs from Turkey Tail, Cordyceps, Reishi, Shiitake, and Agaricus mushrooms by a holistic veterinarian and master herbalist. Medicinal mushrooms like these have been used for thousands of years in Chinese medicine as well as traditional herbalism. Researchers around the globe are now studying their potential in helping with cancer, balancing the immune system, and helping with digestive problems and more.

Natures Immuno Medicinal Mushroom blend for dogs also helps:
Medicinal mushrooms and mushroom extracts are used worldwide to help fight cancer and to help enhance and modulate the immune response of both people and animals. NHV’s mushroom blend contains 5 species of medicinal mushrooms for dogs, which have a long history of use, are well studied, and have been credited with having success against cancer as well as having antioxidant, hypocholesterolemia, anti-tumor, immunomodulatory, anti-allergic, nephroprotective, prebiotic, immunostimulant, anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular, and anti-diabetic properties
Properties of these Medicinal Mushrooms
Benefits of Natures Immuno Medicinal Mushrooms Blend for Dogs
You can read more about medicinal mushrooms for dogs and how they help give added support to pets for cancer and immunity.
NHV carries a wide range of holistic, natural vet-approved remedies that provide support along with a vet-recommended treatment plan. If you have questions about any of our plant-based supplements, ask an NHV expert, because, at NHV, we want your pet to live healthier and longer naturally.
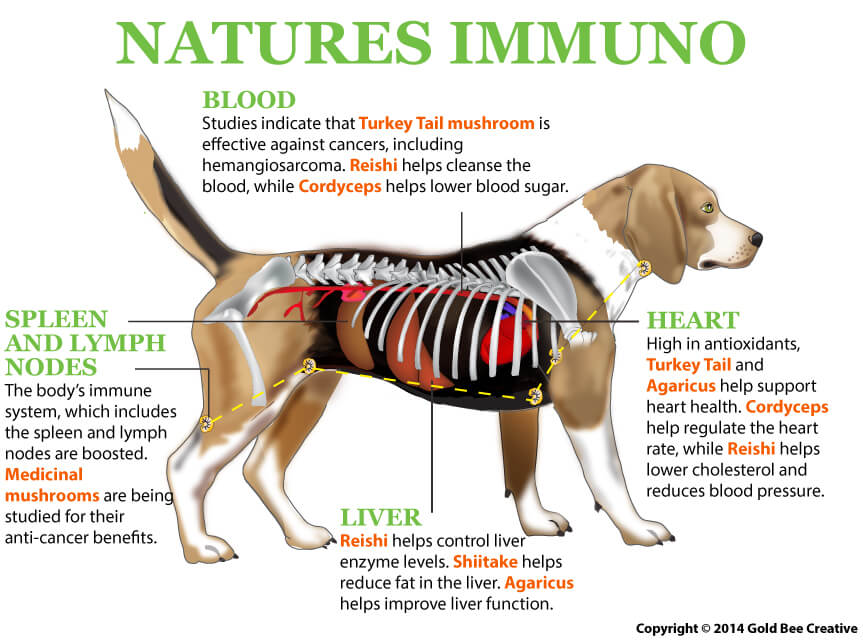
Turkey Tail mushroom is native to Asia, North America, and Europe. It has a long history of use in traditional herbalism and is currently being studied for its health benefits, including its value in fighting cancer. Research has shown that Turkey Tail is beneficial for many types of cancer as it contains properties that help fight cancer cells while helping to strengthen the immune system. Turkey tail mushroom for dogs has shown to be beneficial in spleen and liver hemangiosarcoma in dogs. It is also useful for heart health, lowering cholesterol, digestive issues, and skin problems.
Cordyceps mushroom is very rich in phytonutrients. Research has indicated that these mushrooms demonstrate anti-tumor, immune enhancing and hypoglycemic activity. It has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-tumor, anti-cancer, antimetastatic, and antiviral properties. It is very useful for diabetes as it helps lower blood sugar. Cordyceps also help enhance lymphocyte activity, which balance the immune system.
Reishi mushroom has been used for thousands of years in traditional Chinese medicine. It helps detoxify the blood, helps lower cholesterol and reduces blood pressure. It is also beneficial for the lymphatic system, which helps with a dog’s immunity.
Shiitake mushroom is a popular ingredient in cooking and is highly valued in traditional herbalism for its immune stimulating properties. It helps reduce fat in the liver, helps lower cholesterol, and is beneficial for heart health as it aids in reducing plaque in the arteries. Shiitake may help inhibit the growth of leukemia cells. Shiitake is also a good source of protein, vitamins, and minerals.
Agaricus mushroom is cultivated widely for dietary supplements and culinary purposes. Agaricus is useful for bone health, and helps with insulin production and helps with liver function. Agaricus is considered an adaptogen, which helps combat stress and supports the endocrine functions. This mushroom is currently used in Japan as an adjunctive with chemotherapy treatments.
Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
To be taken twice daily.
Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. You can safely double the recommended dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb 0.5 mL
16 - 30 lb 1.0 mL
31 - 45 lb 1.5 mL
46 - 60 lb 2.0 mL
61 - 75 lb 2.5 mL
Over 75 lb 3.0 mL
For small animals (rabbits, ferrets), avians and reptiles use 1 drop for every 2 lb of body weight.
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provided and place the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth. Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken, yogurt, or a favorite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and well-being of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Natures Immuno Medicinal Mushroom blend for dogs also helps:
Medicinal mushrooms and mushroom extracts are used worldwide to help fight cancer and to help enhance and modulate the immune response of both people and animals. NHV’s mushroom blend contains 5 species of medicinal mushrooms for dogs, which have a long history of use, are well studied, and have been credited with having success against cancer as well as having antioxidant, hypocholesterolemia, anti-tumor, immunomodulatory, anti-allergic, nephroprotective, prebiotic, immunostimulant, anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular, and anti-diabetic properties
Properties of these Medicinal Mushrooms
Benefits of Natures Immuno Medicinal Mushrooms Blend for Dogs
You can read more about medicinal mushrooms for dogs and how they help give added support to pets for cancer and immunity.
NHV carries a wide range of holistic, natural vet-approved remedies that provide support along with a vet-recommended treatment plan. If you have questions about any of our plant-based supplements, ask an NHV expert, because, at NHV, we want your pet to live healthier and longer naturally.

Turkey Tail mushroom is native to Asia, North America, and Europe. It has a long history of use in traditional herbalism and is currently being studied for its health benefits, including its value in fighting cancer. Research has shown that Turkey Tail is beneficial for many types of cancer as it contains properties that help fight cancer cells while helping to strengthen the immune system. Turkey tail mushroom for dogs has shown to be beneficial in spleen and liver hemangiosarcoma in dogs. It is also useful for heart health, lowering cholesterol, digestive issues, and skin problems.
Cordyceps mushroom is very rich in phytonutrients. Research has indicated that these mushrooms demonstrate anti-tumor, immune enhancing and hypoglycemic activity. It has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-tumor, anti-cancer, antimetastatic, and antiviral properties. It is very useful for diabetes as it helps lower blood sugar. Cordyceps also help enhance lymphocyte activity, which balance the immune system.
Reishi mushroom has been used for thousands of years in traditional Chinese medicine. It helps detoxify the blood, helps lower cholesterol and reduces blood pressure. It is also beneficial for the lymphatic system, which helps with a dog’s immunity.
Shiitake mushroom is a popular ingredient in cooking and is highly valued in traditional herbalism for its immune stimulating properties. It helps reduce fat in the liver, helps lower cholesterol, and is beneficial for heart health as it aids in reducing plaque in the arteries. Shiitake may help inhibit the growth of leukemia cells. Shiitake is also a good source of protein, vitamins, and minerals.
Agaricus mushroom is cultivated widely for dietary supplements and culinary purposes. Agaricus is useful for bone health, and helps with insulin production and helps with liver function. Agaricus is considered an adaptogen, which helps combat stress and supports the endocrine functions. This mushroom is currently used in Japan as an adjunctive with chemotherapy treatments.
Select your pet's weight to determine the correct dose.
To be taken twice daily.
Determine your pet’s weight and then use the easy chart below to determine the correct dose. You can safely double the recommended dosage.
Pet's Weight Dosage
0 - 15 lb 0.5 mL
16 - 30 lb 1.0 mL
31 - 45 lb 1.5 mL
46 - 60 lb 2.0 mL
61 - 75 lb 2.5 mL
Over 75 lb 3.0 mL
For small animals (rabbits, ferrets), avians and reptiles use 1 drop for every 2 lb of body weight.
How to Administer
Shake well before use. The easiest method is to use the dropper provided and place the drops into your pet’s food or favorite treat. You can also use the dropper and squirt directly into the pet’s mouth. Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the drops in foods most pet’s love such as fish, chicken, yogurt, or a favorite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak a few kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Herbal dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and well-being of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural herbal supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products are pure herbal extracts and contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
overall vitality

For Overall Health and Well-Being
buy 2 and save $3
Support your dog’s health with omega 3 fish oil for dogs. Help them maintain a healthy coat, eyes, joints, immune system and overall organ function.


Support your dog’s health with omega 3 fish oil for dogs. Help them maintain a healthy coat, eyes, joints, immune system and overall organ function.

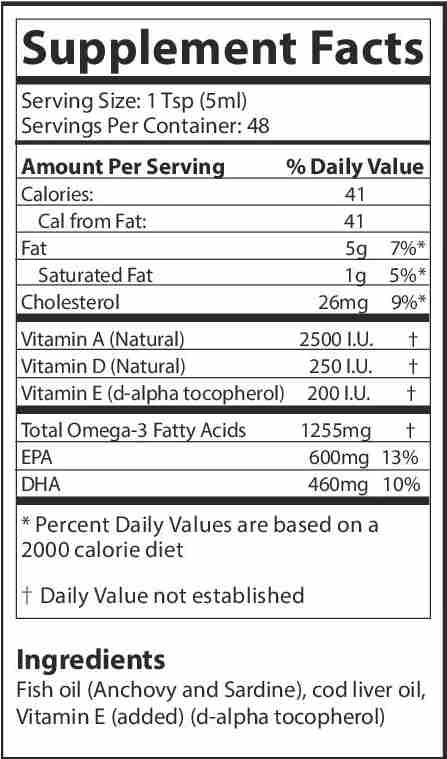
Our omega 3 fish oil for dogs is a great source of EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid 600mg) and DHA (Docosahexaenoic acid 460mg) essential fatty acids. This fish oil supplement for dogs is derived from sardines, anchovies and North Atlantic cod liver oil. It is molecularly distilled and cold pressed to improve the bioavailability of the omega 3 fatty acids, and is medical and human grade quality.
Omega 3 fish oil for dogs may be beneficial for the following:
Processed pet foods have increased omega-6 fatty acids, and decreased omega-3 fatty acids. The University of Maryland Medical Center states, "It is very important to maintain a balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids in the diet. A proper balance helps maintain and even improve health." Your dog’s body cannot easily make essential fatty acids. It is vital to provide omega 3 fish oil for dogs as an added supplement to your pet’s daily diet.
The American Journal of Veterinary Medicine has published studies on the benefits of omega 3 fatty acids (fish oils) for arthritis and degenerative joint disease in dogs. The studies showed that dogs who were given omega 3 fatty acids had a significantly improved ability to get up from a resting position and marked improvement in walking ability.
Suggested Dosage: To be taken once per day. Add to food based on weight chart.
Therapeutic Dosage: Double the quantity for maximum period of 4 weeks or follow veterinarian advise.
Pet’s Weight Dosage
0-15 lb = ¼ tsp
15-30 lb = ½ tsp
30-60 lb = 1 tsp
60-90 lb = 1 ½ tsp
How to Administer: Shake well before use. The easiest method is to add the dosage to your pets food. Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the appropriate amount in food most pet’s love such as fish, chicken, yogurt, or a favorite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and well-being of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Avoid During Pregnancy.
Our omega 3 fish oil for dogs is a great source of EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid 600mg) and DHA (Docosahexaenoic acid 460mg) essential fatty acids. This fish oil supplement for dogs is derived from sardines, anchovies and North Atlantic cod liver oil. It is molecularly distilled and cold pressed to improve the bioavailability of the omega 3 fatty acids, and is medical and human grade quality.
Omega 3 fish oil for dogs may be beneficial for the following:
Processed pet foods have increased omega-6 fatty acids, and decreased omega-3 fatty acids. The University of Maryland Medical Center states, "It is very important to maintain a balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids in the diet. A proper balance helps maintain and even improve health." Your dog’s body cannot easily make essential fatty acids. It is vital to provide omega 3 fish oil for dogs as an added supplement to your pet’s daily diet.
The American Journal of Veterinary Medicine has published studies on the benefits of omega 3 fatty acids (fish oils) for arthritis and degenerative joint disease in dogs. The studies showed that dogs who were given omega 3 fatty acids had a significantly improved ability to get up from a resting position and marked improvement in walking ability.

Suggested Dosage: To be taken once per day. Add to food based on weight chart.
Therapeutic Dosage: Double the quantity for maximum period of 4 weeks or follow veterinarian advise.
Pet’s Weight Dosage
0-15 lb = ¼ tsp
15-30 lb = ½ tsp
30-60 lb = 1 tsp
60-90 lb = 1 ½ tsp
How to Administer: Shake well before use. The easiest method is to add the dosage to your pets food. Some pets can be finicky, if this occurs consider hiding the appropriate amount in food most pet’s love such as fish, chicken, yogurt, or a favorite treat. If your pet only eats dry food then soak kibbles at feeding time.
For Best Results
Dietary supplements are beneficial to the health and well-being of your pet and are safe for long-term use. Every pet responds to natural supplements differently, therefore it is important to be consistent and administer the product daily. Supplements generally take two to four weeks to take effect, however this will vary from one animal to the next.
Product Storage
All NHV Natural Pet Products contain no artificial additives, preservatives or coloring. Shelf life after opening is 6 months and must be refrigerated after opening.
Cautions and Contraindications
Avoid During Pregnancy.

ES Clear -Helps support your pets immune system and over all wellbeing

ES Clear -Helps support your pets immune system and over all wellbeing